
歯が痛くなったり痛くなくなったり…波があるのはなぜ?
歯の痛みは絶えることのできない痛みと一般的に言われています。歯や歯を支える組織の神経はほとんどが脳から直接出ている神経で支配されており、他の体の部位の痛みよりも過敏に感じるからです。歯が痛くなったり、痛くなくなったり、波があるのはなぜでしょうかなのでしょうか。
歯が痛いと感じる時の痛みの原因の種類
歯そのものが原因
歯の構造として、外側からエナメル質、象牙質、歯髄(歯の神経)の3層構造になっております。エナメル質には痛みを伝導する構造はありませんが、象牙質には象牙細管という神経につながる細い管が走っています。よって虫歯や歯が削れることによって象牙質が露出すると、象牙細管から刺激が歯髄に伝わり、痛みが生じることがあります。歯の神経に炎症が到達した場合はさらに痛みが生じる可能性が増します。
歯の周りの組織が原因
歯の周りの組織のことを歯周組織といいます。歯周組織にはセメント質(歯の根の部分にある構造)、歯槽骨(歯を支える骨)、歯肉、歯根膜(歯と骨を介在する膜)があり、この歯周組織に炎症が起こると、歯の周りの存在する組織のため、歯が痛いと感じることがあります。歯周組織の炎症で代表的なものが、歯周病です。歯周病はお口の中の細菌が毒素を出し、歯周組織を侵していきます。
歯や歯の周りの組織以外が原因
歯や歯周組織が原因ではなくとも、歯が痛いと感じることがあります。例えば、お口の中にできるできもので、良性腫瘍や悪性腫瘍が存在すると、歯や歯周組織の神経を刺激して痛みを感じることがあります。また、上顎の歯は上顎洞という鼻の空洞の一部に近接しています。鼻炎等が原因で上顎洞に炎症が起こると、歯が痛いと感じることがあります。
歯が痛くなったり痛くなくなったりする場合の具体例
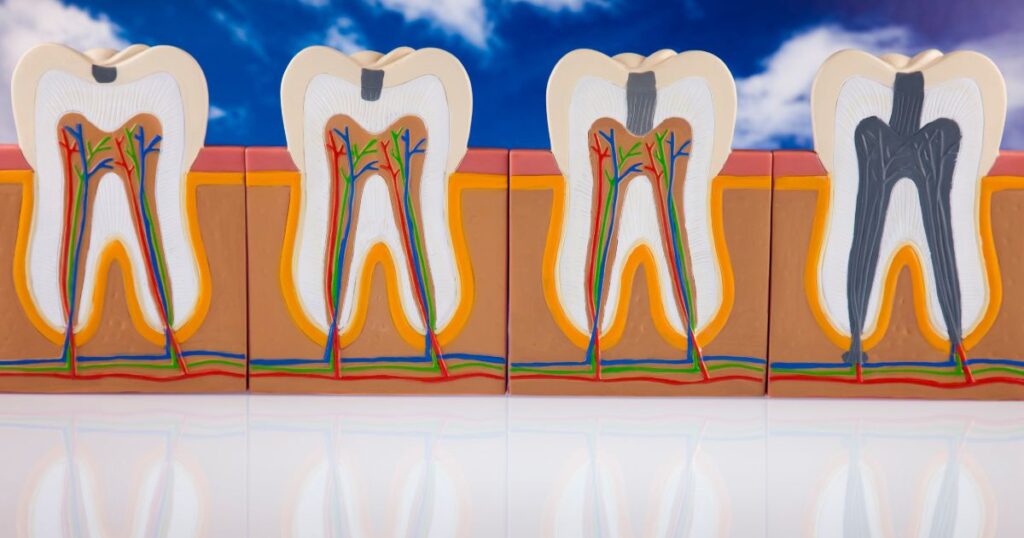
虫歯が進行して神経に影響を与えている
虫歯が進行していくと、エナメル質から、象牙質、象牙質から歯髄に向かって虫歯は進行していきます。虫歯が象牙質に達すると、象牙細管があるため、刺激が神経に伝わり、痛みを生じたり、消失したりを繰り返す可能性があります。歯髄に近接すればするほど、理論的には痛みが出る可能性が高くなりますが、歯の構造は個人差があるため、歯髄に近接している場合でも痛みが生じない場合もありますし、逆に歯髄に近接していなくても痛みが生じることがあります。虫歯の進行に対する痛みは、痛みに慣れてくると消失する可能性もあります。
神経の炎症が強すぎて、神経が死んでしまった場合
神経の炎症が強い時は、もちろん痛みが生じる場合が多いですが、神経の炎症が強すぎて、神経が死んでしまった場合はいきなり痛みが消失することもあります。痛みが消失すると、それは状態が良くなったと勘違いすることが多いですが、むしろ悪化していると考えた方が良いでしょう。歯の強い痛みの後、突然痛みが消えた場合は神経が死んでしまった可能性が高いため、すぐに歯科医院を受診することをお勧めします。神経が死んだ後、さらに炎症が進むと、歯周組織まで炎症が広がるため、再び痛みが生じることもあります。
歯周病や親知らずの炎症が起きている
歯周病や親知らずの炎症はお口の中の汚れが原因でおきます。炎症が強くなると、痛みや腫れを生じることがありますが、自分の免疫力が勝る場合は、やがて痛みや腫れが消失することもあります。一度痛みや腫れが消失したからといって、治療せずに放置すると、一定の期間後に再度痛みや腫れが生じることがあります。
歯ぎしりや噛み合わせの問題がある
歯ぎしりや噛み合わせによって、ある特定の歯の部位に力がかかると、痛みが生じたり、消失したりを繰り返すことがあります。これは、歯周組織の一部である歯根膜に負担がかかることによって、歯根膜が肥厚し、炎症が起こることに起因します。痛みが生じることによって、その部位を避けて生活するようになるため、やがて歯根膜の肥厚は消失することが多いですが、場合によっては歯の破折に繋がることもあります。
ストレスや体調の変化によって痛みの感度が変わっている
ストレスが原因で歯が痛くなる原因は様々あります。まず人がストレスや体調の変化によって、体の中の交感神経が優位になります。これによって、お口の中に本来出てくるはずの唾液の量が減少します。唾液はお口の中を健康に保つために大きな役割を果たしています。
例えば、唾液の中にはリゾチームというお口の中の細菌に抵抗する抗菌物質、免疫作用を発揮するIgAという物質が入っています。これらが減少することによって、虫歯や歯周病に発生するリスクは数段高くなります。また、唾液にはお口の粘膜を守るムチンという物質が入っており、これが減少することによってお口の中が乾燥し、ヒリヒリすることもありますし、酸によって溶解した歯のカルシウムを、再び歯に沈着させる作用も唾液には含まれるため、その作用が低下することによって、歯がしみるようになる可能性も上がります。
ストレスや体調の変化によって神経そのものが過敏になり、虫歯や歯周病などの具体的な疾患がないにも関わらず、痛みを生じたり、消失したりを繰り返すこともあります。歯の神経は脳から出ています。脳は神経の集合体なので、神経が過敏になると、一番最初に脳や脳から出る神経に影響を及ぼすからです。
そもそも歯が痛くならないために
そもそも歯が痛くならないためには、どうすれば良いのでしょうか。定期的に歯科医院に通っていればそれで良いのでしょうか。もちろん定期的に歯科医院に通うことは、虫歯や歯周病の早期発見には大切ですが、一番大切なのは毎日のセルフケアです。毎日のセルフケアがおろそかになると、どんなに一生懸命歯科医院に定期的に通っていても、歯が悪くなることがあります。適切なセルフケアを習得するためにも、自分にあったセルフケアを提案してくれる歯科医院を探したり、わからないことや疑問に思うことは、自ら歯科医師や歯科衛生士に質問する姿勢も大切です。
まとめ
歯の痛みは病態的な問題だけでなく、日常生活にも大きく影響します。歯の痛みを生じることによって、仕事ができなくなったり、食事もまともに取ることができなくなります。歯の痛みを出さないためにも、定期的に歯科医院に検診に行くだけでなく、自分に合ったセルフケアを習得するようにしましょう。
 執筆 歯科医師/issy
執筆 歯科医師/issy
国立歯学部卒業後、東京医科歯科大学歯学部附属病院で研修、現在勤務医として一般歯科、矯正歯科に携わっている。
日本口腔インプラント学会所属



















